LM Studio 0.3.10: 🔮 推測的デコーディング
M3 MacBook ProでLlama 8Bをメイン、Llama 1Bをドラフトとして、両方MLX 4ビット
LM Studioのllama.cppおよびMLXエンジンで推測的デコーディングをサポートすることをお知らせできて大変嬉しく思います!
推測的デコーディングは、場合によってはトークン生成を最大1.5倍から3倍高速化できる技術です。
LM Studioを0.3.10にアプリ内アップデートで、またはhttps://lmstudio.dokyumento.jp/downloadからアップグレードしてください。
推測的デコーディング
推測的デコーディングは、Leviathan et al.によるFast Inference from Transformers via Speculative DecodingやChen et al.によるAccelerating Large Language Model Decoding with Speculative Samplingといった研究によって開拓された推論最適化技術です。これは、現代のCPUに見られるような投機的実行最適化の一種と見なすことができますが、LLMの推論に適用されています。
LM Studioのllama.cppとMLXの両エンジンでは、推測的デコーディングは2つのモデルの組み合わせによって実装されています。1つはより大きなLLM(「メインモデル」)、もう1つはより小さく高速な「ドラフトモデル」(または「投機モデル」)です。元のllama.cppの実装はGeorgi Gerganovによって、MLXの実装はBenjamin AndersonとAwni Hannunによって作成されました。これらの実装はオープンソースコミュニティによって継続的に改善されています。
動作原理
まずドラフトモデルが実行され、次のいくつかのトークンを「ドラフト」生成として素早く予測します。その後すぐに、ドラフト生成されたトークンはメインモデルによって確認または却下されます。メインモデルが生成したであろうトークンのみが受け入れられます。これにより、(十分なトークンが受け入れられた場合) 品質を低下させることなく高速化が実現されます。トークンが却下される頻度が高い場合は、全体的な生成速度が低下する可能性があります!最良の結果を得るためには、モデルの選択が重要です。
パフォーマンス統計
LM Studio + MLXエンジン (Apple M3 Pro, 36GB RAM)
| プロンプト | メインモデル | ドラフトモデル | 推測的デコーディングなし | 推測的デコーディングあり | トークン/秒の高速化 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| "Pythonでクイックソートアルゴリズムを作成してください。コードのみを記述してください。" | Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct-MLX-4bit | Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct-4bit | 7.30トークン/秒 | 17.74トークン/秒 | 2.43倍 |
| "ピタゴラスの定理を説明してください" | Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-4bit | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit | 29.65トークン/秒 | 50.91トークン/秒 | 1.71倍 |
| "ワシントンDCへの1日旅行を計画してください" | Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-4bit | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit | 29.94トークン/秒 | 51.14トークン/秒 | 1.71倍 |
LM Studio + CUDA llama.cppエンジン (NVIDIA RTX 3090 Ti 24GB VRAM, Intel Core Ultra 7 265K CPU, 32GB RAM)
| プロンプト | メインモデル | ドラフトモデル | 推測的デコーディングなし | 推測的デコーディングあり | トークン/秒の高速化 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| "Pythonでクイックソートアルゴリズムを作成してください。コードのみを記述してください。" | Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct-GGUF (Q4_K_M) | Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct-GGUF (Q4_K_M) | 21.84トークン/秒 | 45.15トークン/秒 | 2.07倍 |
| "ピタゴラスの定理を説明してください" | Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF (Q8_0) | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-GGUF (Q4_0) | 50.11トークン/秒 | 68.40トークン/秒 | 1.36倍 |
| "ワシントンDCへの1日旅行を計画してください" | Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct-GGUF (Q8_0) | Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-GGUF (Q4_0) | 46.90トークン/秒 | 49.09トークン/秒 | 1.05倍 |
チャットで推測的デコーディングを使用する
LM Studio 0.3.10では、推測的デコーディングの新しいサイドバーセクションが追加されています。メインモデルを読み込むと(cmd/ctrl + L)、新しいドラフトモデルセレクターに互換性のあるドラフトモデルのオプションが表示されます。
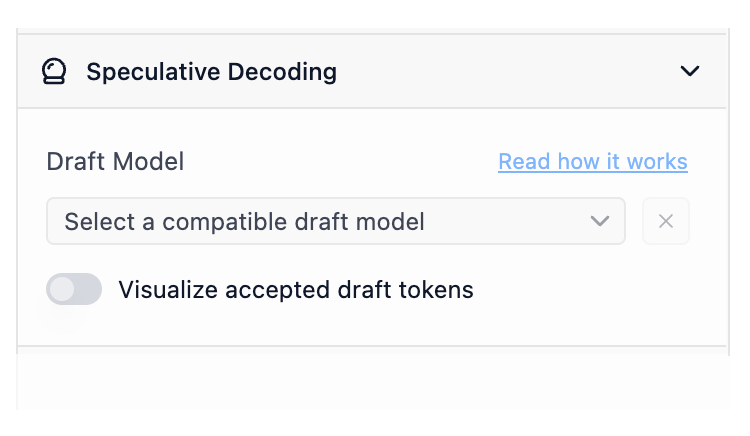
設定サイドバーの新しいドラフトモデルセレクター
ドラフトモデルの互換性
あるモデルを別のモデルのドラフトモデルとして使用するには、それらが「互換性がある」必要があります。大まかに言えば、ドラフトモデルが効果的であるためには、より大きなモデルが生成する可能性のある同じトークンから生成できる必要があります。実用的に言えば、両方のモデルは十分に類似した語彙(モデルが「知っている」トークンの総体)とトークナイザー特性を共有する必要があります。LM Studioは、推測的デコーディングの目的で、モデル同士が互換性があるかどうかを自動的にチェックします。
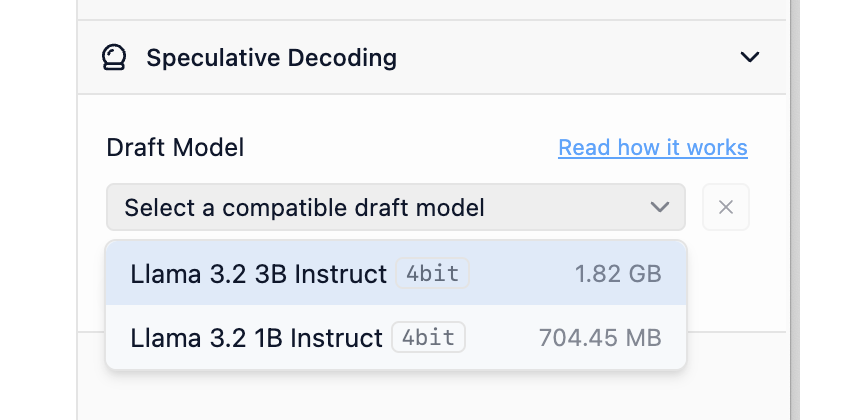
LM Studioは、可能なメインモデルとドラフトモデルのペアの互換性を自動的にインデックス化します。
受け入れられたドラフトトークンを視覚化
受け入れられたドラフトトークンの視覚化をオンにすると、それらがドラフトモデルまたはメインモデルのどちらから生成されたかを示す色付きのトークンが表示されます。緑色が濃いほど、良好です。
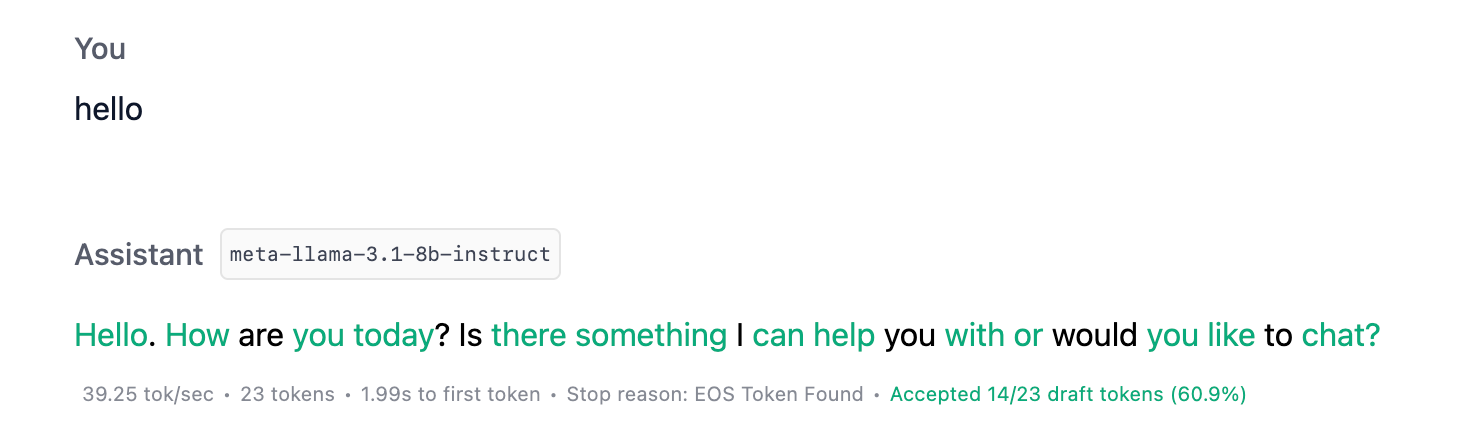
ドラフトモデルのパフォーマンスをより理解するために、ドラフトトークン受け入れの視覚化をオンにします。
API経由で推測的デコーディングを使用する
LM Studioのローカルサーバー経由で推測的デコーディングを使用することもできます。有効にすると、推測的デコーディングに関連する新しいフィールドを含む豊富な生成統計が返されます。
"stats": { "tokens_per_second": 15.928616628606926, "time_to_first_token": 0.301, "generation_time": 1.382, "stop_reason": "stop", "draft_model": "lmstudio-community/llama-3.2-1b-instruct", "total_draft_tokens_count": 12, "accepted_draft_tokens_count": 10, "rejected_draft_tokens_count": 0, "ignored_draft_tokens_count": 2 }
LM StudioのREST APIから返される統計。詳細についてはこちらをご覧ください。
オプション1: サーバーUIでドラフトモデルを設定する
チャットと同様に、設定サイドバーでドラフトモデルを設定できます。設定すると、このモデルをターゲットとするリクエストは、選択したドラフトモデルを使用して推測的デコーディングを活用します。
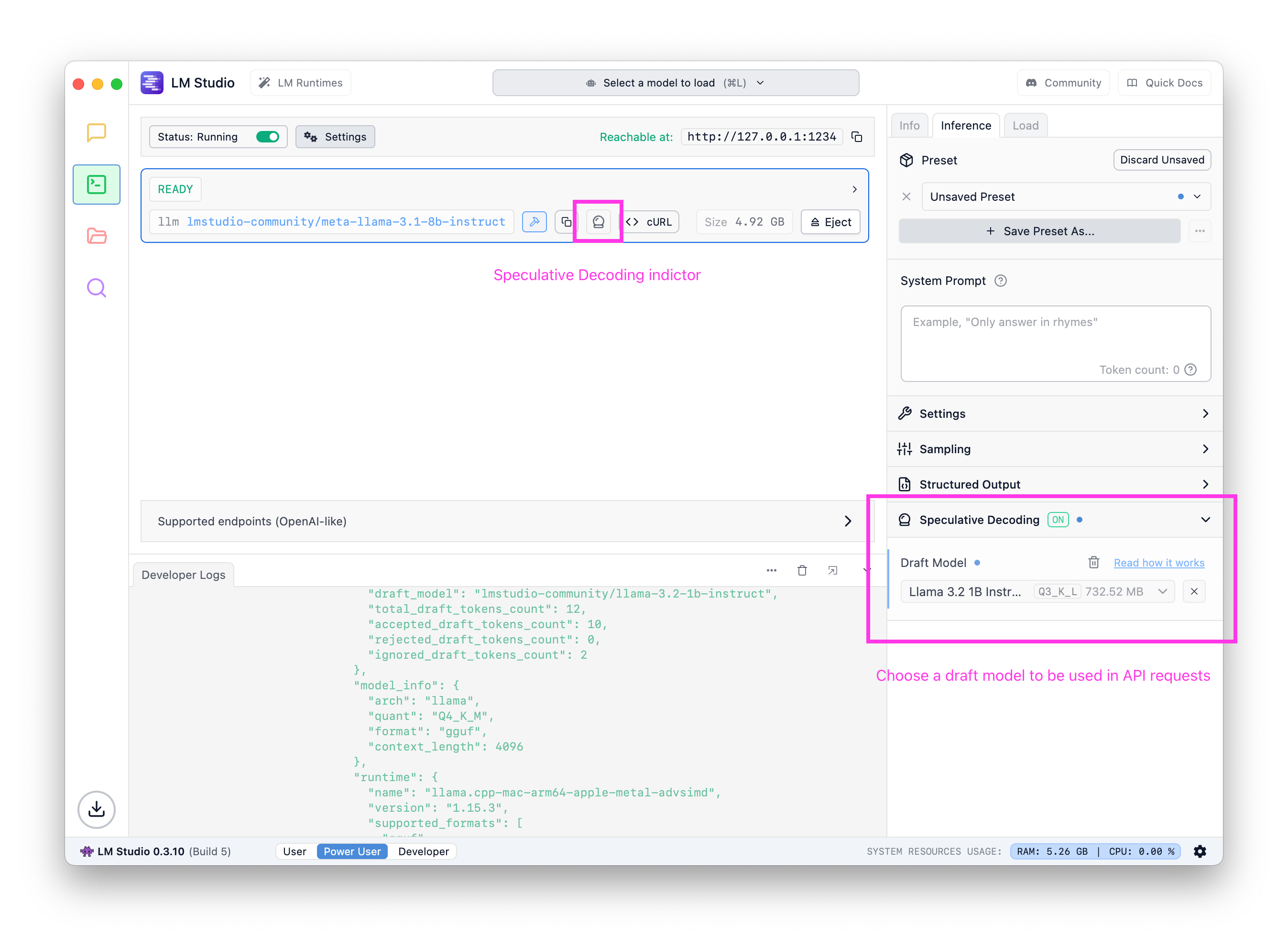
サーバーUIで、任意のメインモデルのデフォルトのドラフトモデルを設定します。
オプション2: リクエストのdraft_model
リクエストのペイロードの一部としてドラフトモデルのキーを提供することもできます。JITローディングについて詳しくはこちらをご覧ください。
curl http://localhost:1234/api/v0/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "deepseek-r1-distill-qwen-7b", + "draft_model": "deepseek-r1-distill-qwen-0.5b", "messages": [ ... ] }'
推測的デコーディングは、LM StudioのOpenAI互換APIとREST APIの両方で利用できます。
推測的デコーディングを効果的に使用する方法
ドキュメント記事「推測的デコーディング」をお読みください。
経験則として、大きなモデルと小さなモデルをペアにすることを目指しましょう。ドラフトモデルはメインモデルよりもはるかに小さく、同じファミリーのものである必要があります。例えば、Llama 3.1 8BのドラフトモデルとしてLlama 3.2 1Bを使用できます。
注: LM Studio 0.3.10現在、システムは、GPUが存在する場合、ドラフトモデルを完全にGPUにオフロードしようとします。メインモデルのGPU設定は通常通り構成可能です。
多くの場合、一部のタスクやモデルでは、品質を損なうことなく2倍以上の高速化を実現できます。
パフォーマンスが低下する可能性のある場合
パフォーマンスが低下する主な要因は2つあります。利用可能なリソースに対してドラフトモデルが大きすぎること、およびドラフト受け入れ率が低いことです。前者を避けるためには、常にメインモデルと比較してはるかに小さいドラフトモデルを使用してください。後者はモデルとプロンプトに依存します。推測的デコーディングの潜在的なトレードオフを理解する最善の方法は、自分が関心のあるタスクで実際に試してみることです。
互換性のあるドラフトモデルの検索
すべてのモデルが互いに互換性があるわけではないため、ドラフトモデルとメインモデルとして連携できるモデルを特定することが重要です。
簡単なアプローチは、以下の表に示すように、同じモデルファミリーの大小のバリアントを使用することです。
| メインモデルの例 | ドラフトモデルの例 |
|---|---|
| Llama 3.1 8B Instruct | Llama 3.2 1B Instruct |
| Qwen 2.5 14B Instruct | Qwen 2.5 0.5B Instruct |
| DeepSeek R1 Distill Qwen 32B | DeepSeek R1 Distill Qwen 1.5B |
プロのヒント:📂マイモデルでデフォルトのドラフトモデルを設定する
特定のドラフトモデルを常に使用したい場合は、マイモデルでモデルごとのデフォルトとして設定できます。これを設定すると、このモデルが使用される際(チャットまたはAPI経由)、選択したドラフトモデルを使用した推測的デコーディングが有効になります。
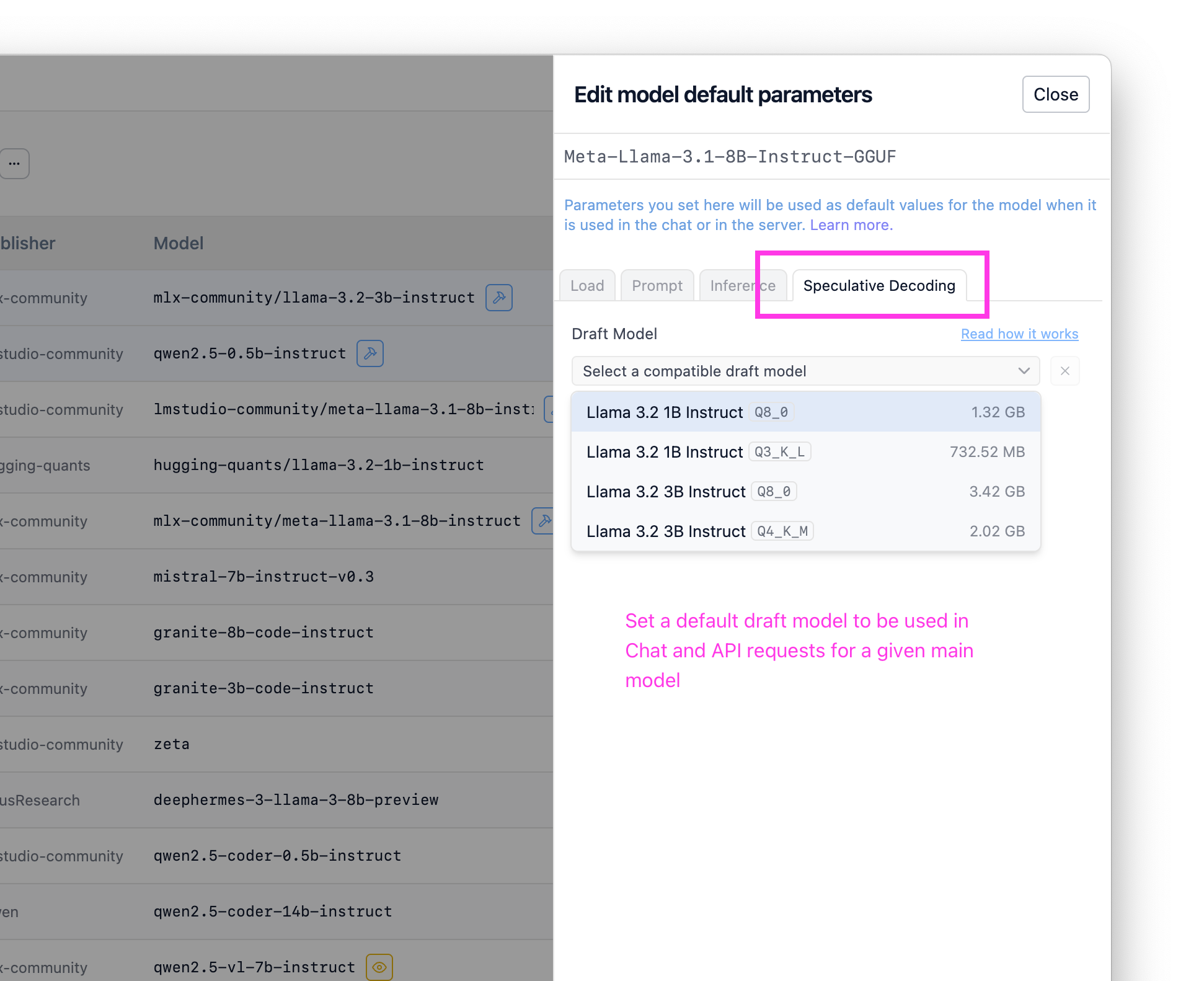
マイモデルで、任意のメインモデルのデフォルトのドラフトモデルを設定します。
高度なリソース
さらに深く掘り下げたい方のために、いくつかの追加リソースをまとめました!
この種の仕事に興味がありますか?採用中です。履歴書と、あなたが誇りに思うプロジェクトに関するメモを[email protected]までお送りください。
論文:
- Fast Inference from Transformers via Speculative Decoding
- Accelerating Large Language Model Decoding with Speculative Sampling
- SpecInfer: Accelerating Large Language Model Serving with Tree-based Speculative Inference and Verification
- Accelerating LLM Inference with Staged Speculative Decoding
互換性チェックの実装
以下は、モデル間の推測的デコーディング互換性をチェックするための現在の実装を示すllama.cppとMLXからの抜粋です。
# The current MLX compat check is very minimal and might evolve in the future
def is_draft_model_compatible(self, path: str | Path) → bool:
path = Path(path)
draft_tokenizer = mlx_lm.tokenizer_utils.load_tokenizer(path)
if draft_tokenizer.vocab_size != self.tokenizer.vocab_size:
return False
return True
出典:
llama.cpp: ggml-org/llama.cppMLX: lmstudio-ai/mlx-engine
0.3.10 - 完全な変更履歴
**Build 6** - Fixed an issue where first message of tool streaming response did not include "assistant" role - Improved error message when trying to use a draft model with a different engine. - Fixed a bug where speculative decoding visualization does not work when continuing a message. **Build 5** - Bug fix: conversations would sometimes be named 'Untitled' regardless of auto naming settings - Update MLX to enable Speculative Decoding on M1/M2 Macs (in addition to M3/M4) - Fixed an issue on Linux and macOS where child processes may not be cleaned up after app exit - [Mac][MLX] Fixed a bug where selecting a draft model during prediction would cause the model to crash **Build 4** - New: Chat Appearance > "Expand chat container to window width" option - This option allows you to expand the chat container to the full width of the window - Fixed RAG not working due to "path must be a string" **Build 3** - The beginning and the end tags of reasoning blocks are now configurable in My Models page - You can use this feature to enable thinking UI for models that don't use `<think>` and `</think>` tags to denote reasoning sections - Fixed a bug where structured output is not configurable in My Models page - Optimized engine indexing for reduced start-up delay - Option to re-run engine compatibility checks for specific engines from the Runtimes UI - [Mac] Improved reliability of MLX runtime installation, and improved detection of broken MLX runtimes **Build 2** - Fixed a case where the message about updating the engine to use speculative decoding is not displayed - Fixed a bug where we sometimes show "no compatible draft models" despite we are still identifying them - [Linux] Fixed 'exit code 133' bug (reference: https://github.com/lmstudio-ai/lmstudio-bug-tracker/issues/285) **Build 1** - New: 🔮 Speculative Decoding! (for llama.cpp and MLX models) - Use smaller "draft model" to achieve generation speed up by up to 1.5x-3x for larger models. - Works best when combining very small draft model + large main model. The speedup comes without _any_ degradation in quality. - Your mileage may vary. Experiment with different draft models easily to find what works best. - Works in both chat UI and server API - Use the new "Visualize accepted draft tokens" feature to watch speculative decoding in action. - Turn on in chat sidebar. - New: Runtime (cmd/ctrl + shift + R) page UI - Auto update runtimes only on app start up - Fixed a bug where multiple images sent to the model would not be recognized
さらに
- macOS、Windows、またはLinux用の最新のLM Studioアプリをダウンロードしてください。
- 職場組織でLM Studioを使用したい場合は、お問い合わせください: LM Studio @ Work
- 議論とコミュニティについては、Discordサーバーにご参加ください。
- LM Studioは初めてですか?ドキュメントをご覧ください: ドキュメント: LM Studio入門。